Example
These examples demonstrate how to use the STD2 operator.
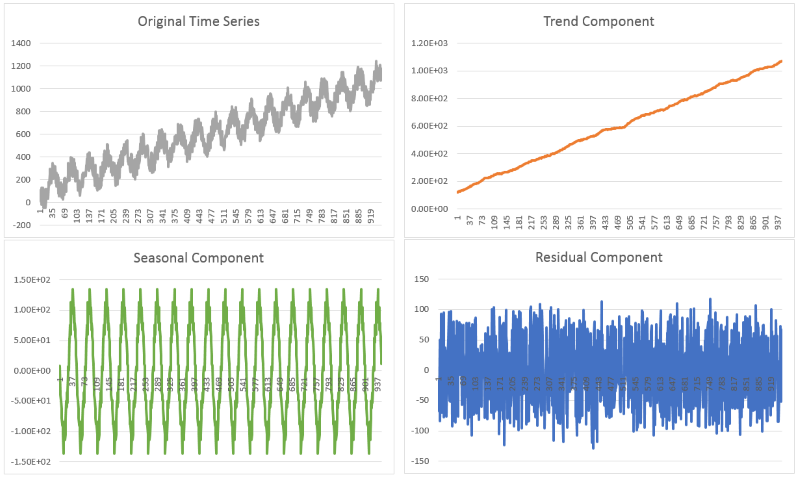
The following example uses the STD2 operator to compute the season, trend and residual from a time series.
use com.teracloud.streams.timeseries.analysis::STD2 ;
composite STD2Example {
graph
stream<float64 data> DataStream = Custom() {
logic
state : {
float64 duration = 1.0f; // 1 second
float64 sample_rate = 1000; // 1000 samples / sec
float64 num_seasons = 20;
float64 amplitude = 100;
float64 delta = 1.0/sample_rate;
}
onProcess : {
mutable float64 t = 0.0;
mutable float64 trend = 1f;
while(t < duration) {
mutable float64 y = amplitude * sin(num_seasons * 2f * PI() * t);
y = y + 200f*random() + trend;
trend += 1f;
t += delta;
submit({data = y}, DataStream);
}
}
}
stream<float64 data, float64 season, float64 trend, float64 residual> STDStream = STD2(DataStream) {
param
inputTimeSeries : data ;
seasonLength : 50u ;
algorithm : Additive ;
numSeasons : 20u ;
output
STDStream : season = season(), trend = trend(), residual = residuals() ;
}
() as STD2ResultSink = FileSink(STDStream) {
param
file : "std2_results.csv" ;
format : csv ;
}
}
The following graph illustrates the results of the decomposed time series: